 |
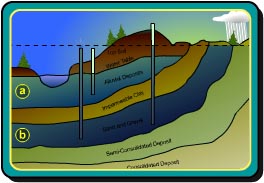
Aquifers may also be classified as unconfined or confined, depending on the presence or absence of a confining layer (a low permeability or nearly impermeable geologic layer). In addition, fractured rocks may be considered "semi-confined," or a complex unconfined aquifer (Risser and Barton, 1995). This condition is a result of the network of fractures and is best seen where a well initially fails to encounter a fracture at the "water table." Once a water-bearing fracture is intersected, the water rises in the borehole to the regional water table because of the amount of pressure applied on a particular set of fractures. The mostly impermeable rock acts as a confining unit to its own fractures. A highly fractured rock may override this effect so that water levels appear more unconfined.